|
排序算法
排序是非常常用,非常基本的算法。排序的方法有很多,比如插入排序、选择排序、希尔排序、归并排序、快速排序、堆排序。
本次试验重点实现:希尔排序、归并排序、快速排序、堆排序
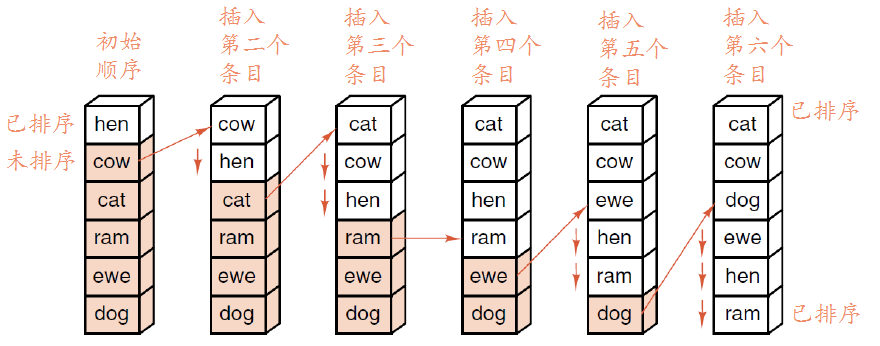
插入排序
简单说就是每次选未排序的队列中最小的条目插入到已排序队列的最后:

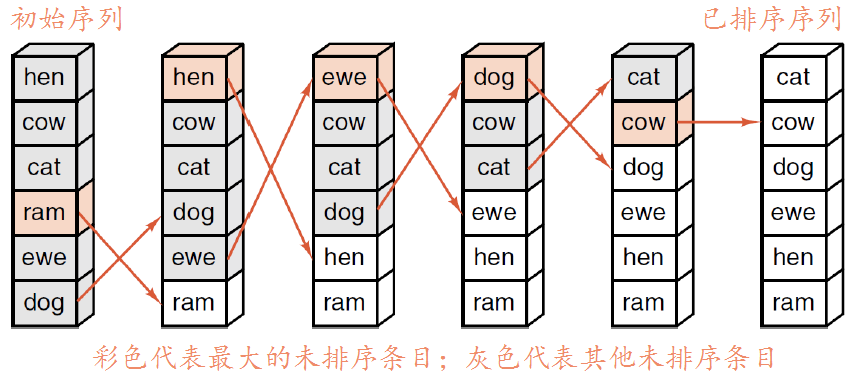
选择排序
选择排序和插入有点像,是每次从拿未排序中的第一个条目插入到已排序中应该插入的位置:

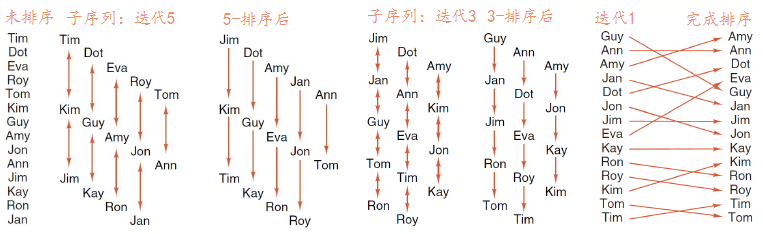
希尔排序
希尔排序是插入排序的一种,是针对直接插入排序算法的改进。
希尔排序的基本思想是:先取一个小于count的增量increment,把表中Record分为increment组,所有距离为increment的Record为同一组,现在各组中进行直接插入排序(insert_sort),然后减小increment重复分组和排序,知道increment=1,即所有Record放在同一组中进行直接插入排序为止。

【相关实验】
首先从类表List中派生子表Sortable_list。为了方便定义,我们可以重载这样的构造函数
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print
?
- template<class?Record>??
-
Sortable_list<Record>::Sortable_list(const?Record?A[],int?size)??
- {??
-
????for(int?i=0;i<size;i++)??
- ????????insert(i,A[i]);??
- }??
template<class Record>
Sortable_list<Record>::Sortable_list(const Record A[],int size)
{
for(int i=0;i<size;i++)
insert(i,A[i]);
}
1.编写函数shell_sort。函数中我们从首先定义increment=0,观察题目要求,可以得到在循环中有这样的关系increment=increment/2;使用循环将每次分组后的每组排列,排列我们再增加函数sort_interval();在每组的排序中使用的直接插入排序,所以可以这样实现sort_interval:每次定义一个临时的Sortable_list对象tmp记录每次分组的小组,对tmp使用insertion_sort,进而我们编写函数insertion_sort();
2.实现表的排序一个重要的步骤是将Record换到相应位置,即交换,所以编写函数swap;
3.为了输出每趟排序结果,我们再编写一个全局函数print_out,由List的成员函数traverse()调用;调用的过程在置于swap之中,即每次有交换(或看做移动)则看做一趟排序。
相应算法函数如下:
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print
?
- template<class?Record>??
-
void?Sortable_list<Record>::shell_sort()??
-
/*Post:?The?entries?of?the?Sortable_list?have?been?rearranged?so?that?the?keys?in??
- ????????all?the?entries?are?sorted?into?nondecreasing?order.?
- ??Uses:?sort_interval.?
- */??
- {??
-
????int?increment,???//spacing?of?entries?in?sublist??
-
????????start;???????//starting?point?of?sublist??
- ????increment=count;??
-
????do{??
- ????????increment=increment/2;??
-
????????for(start=0;start<increment;start++){??
-
????????????sort_interval(start,increment);??//modified?insertion?sort??
- ????????????traverse(print_out);??
- ????????????cout<<endl;??
- ????????}??
-
????}while(increment>1);??
- }??
- ??
-
template<class?Record>??
-
void?Sortable_list<Record>::sort_interval(int?start,int?increment)??
- {??
- ????Sortable_list<Record>?temp;??
-
????int?j=0;??
-
????for(int?i=start;i<size();i=i+increment){??
- ????????Record?temp_record;??
- ????????retrieve(i,temp_record);??
- ????????temp.insert(j,temp_record);??
- ????????j++;??
- ????}??
- ????temp.insertion_sort();??
- ????j=0;??
-
????for(int?k=start;k<size();k+=increment){??
- ????????Record?temp_record;??
- ????????temp.retrieve(j,temp_record);??
- ????????replace(k,temp_record);??
- ????????j++;??
- ????}??
- }??
-
template<class?Record>??
-
void?Sortable_list<Record>::insertion_sort()??
-
/*Post:?The?entries?of?the?Sortable_list?have?been?rearranged?so?that?the?keys?in?
- ????????all?the?entries?are?sorted?into?nondecreasing?order.?
- ??Uses:?Methods?for?the?class?Record;?the?contiguous?List??
- */??
- {??
-
????int?first_unsorted;????????????//position?of?first?unsorted?entry??
-
????int?position;??????????????????//searches?sorted?part?of?list??
-
????Record?current;????????????????//holds?the?entry?emporarily?removed?from?list??
-
????for(first_unsorted=1;first_unsorted<count;first_unsorted++)??
-
????????if(entry[first_unsorted]<entry[first_unsorted-1]){??
- ????????????position=first_unsorted;??
-
????????????current=entry[first_unsorted];?//Pull?unsorted?entry?out?of?the?list.??
-
????????????do{????????????????????//Shift?all?entries?until?the?proper?position?is?found??
- ????????????????entry[position]=entry[position-1];??
-
????????????????position--;?????????//position?if?empty.??
-
????????????}while(position>0&&entry[position-1]>current);??
- ????????????entry[position]=current;??
- ????????}??
- }??
-
//其他辅助函数见源文件??
template<class Record>
void Sortable_list<Record>::shell_sort()
/*Post: The entries of the Sortable_list have been rearranged so that the keys in
all the entries are sorted into nondecreasing order.
Uses: sort_interval.
*/
{
int increment,//spacing of entries in sublist
start; //starting point of sublist
increment=count;
do{
increment=increment/2;
for(start=0;start<increment;start++){
sort_interval(start,increment); //modified insertion sort
traverse(print_out);
cout<<endl;
}
}while(increment>1);
}
template<class Record>
void Sortable_list<Record>::sort_interval(int start,int increment)
{
Sortable_list<Record> temp;
int j=0;
for(int i=start;i<size();i=i+increment){
Record temp_record;
retrieve(i,temp_record);
temp.insert(j,temp_record);
j++;
}
temp.insertion_sort();
j=0;
for(int k=start;k<size();k+=increment){
Record temp_record;
temp.retrieve(j,temp_record);
replace(k,temp_record);
j++;
}
}
template<class Record>
void Sortable_list<Record>::insertion_sort()
/*Post: The entries of the Sortable_list have been rearranged so that the keys in
all the entries are sorted into nondecreasing order.
Uses: Methods for the class Record; the contiguous List
*/
{
int first_unsorted; //position of first unsorted entry
int position; //searches sorted part of list
Record current; //holds the entry emporarily removed from list
for(first_unsorted=1;first_unsorted<count;first_unsorted++)
if(entry[first_unsorted]<entry[first_unsorted-1]){
position=first_unsorted;
current=entry[first_unsorted]; //Pull unsorted entry out of the list.
do{ //Shift all entries until the proper position is found
entry[position]=entry[position-1];
position--; //position if empty.
}while(position>0&&entry[position-1]>current);
entry[position]=current;
}
}
//其他辅助函数见源文件
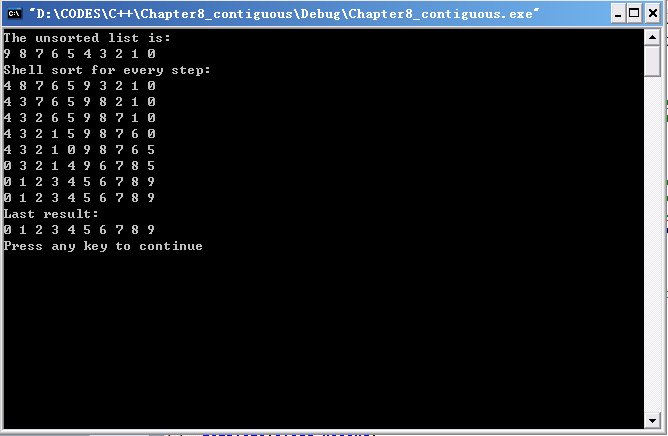
【实验结果】

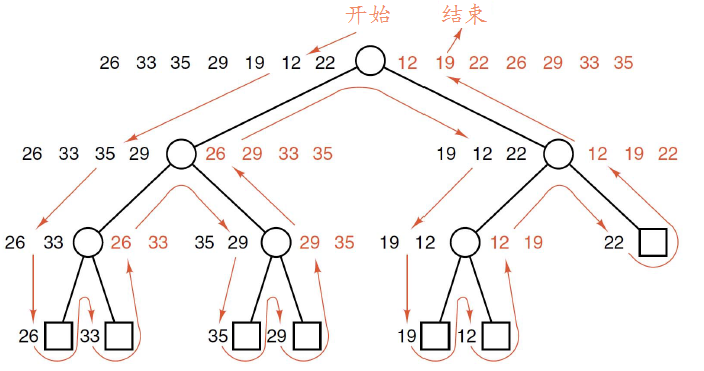
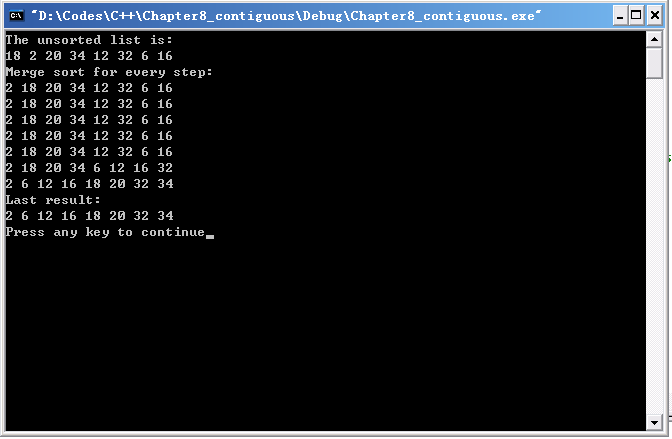
归并排序
归并排序是采用分治的思想将两个已排序的表合并成一个表
归并排序算法的基本思想是:先将一个表分成两个表(当个数是奇数时,使左表的元素比右表多一)。对两个表分别进行归并排序,然后将两个已排序好的表合并。合并的思路就像将两罗纸牌混成一摞,每次取顶上最小的纸牌。

【相关实验】
1.仍旧使用上述的Sortable_list
2.根据归并排序的思想,每次子表仍旧使用归并排序,可以通过递归实现。所以编写递归函数recursive_merge_sort(),要把已排序好的子表合并,所以编写合并子表的辅助函数merge()
3.为了输出每趟排序结果,在归并时merge中加入traverse(print_out) ?//但因为递归调用的问题,很多次我们还是看不到过程
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print
?
- template<class?Record>??
-
void?Sortable_list<Record>::merge(int?low,int?high)??
- {??
-
????Record?*tmp=new?Record[high-low+1];??
-
????int?index=0;??
-
????int?index1=low,mid=(low+high)/2,index2=mid+1;??
-
????while(index1<=mid&&index2<=high){??
-
????????if(entry[index1]<entry[index2])??
- ????????????tmp[index++]=entry[index1++];??
-
????????else??
- ????????????tmp[index++]=entry[index2++];??
- ????}??
-
????while(index1<=mid)??
- ????????tmp[index++]=entry[index1++];??
-
????while(index2<=high)??
- ????????tmp[index++]=entry[index2++];??
-
????for(index=low;index<=high;index++)??
- ????????entry[index]=tmp[index-low];??
-
????delete?[]tmp;??
- ????traverse(print_out);??
- ????cout<<endl;??
- ??????
- }??
- ??
-
template<class?Record>??
-
void?Sortable_list<Record>::recursive_merge_sort(int?low,int?high)??
-
/*Post:?The?entries?of?the?sortable?list?between?
- ????????index?low?and?high?have?been?rearranged?so?that?
- ????????their?keys?are?sorted?into?nondecreasing?order.?
- ??Uses:?The?contiguous?list?
- */??
- {??
-
????if(high>low){??
- ????????recursive_merge_sort(low,(high+low)/2);??
- ????????recursive_merge_sort((high+low)/2+1,high);??
- ????????merge(low,high);??
- ????}??
- }??
- ??
-
template<class?Record>??
-
void?Sortable_list<Record>::merge_sort()??
-
/*?Post:?The?entries?of?the?sortable?list?have?been?rearranged?so?that?
- ?????????their?keys?are?sorted?into?nondecreasing?order.?
- ???Uses:?The?contiguous?list?
- */??
- {??
- ????recursive_merge_sort(0,size()-1);??
- }??
template<class Record>
void Sortable_list<Record>::merge(int low,int high)
{
Record *tmp=new Record[high-low+1];
int index=0;
int index1=low,index2=mid+1;
while(index1<=mid&&index2<=high){
if(entry[index1]<entry[index2])
tmp[index++]=entry[index1++];
else
tmp[index++]=entry[index2++];
}
while(index1<=mid)
tmp[index++]=entry[index1++];
while(index2<=high)
tmp[index++]=entry[index2++];
for(index=low;index<=high;index++)
entry[index]=tmp[index-low];
delete []tmp;
traverse(print_out);
cout<<endl;
}
template<class Record>
void Sortable_list<Record>::recursive_merge_sort(int low,int high)
/*Post: The entries of the sortable list between
index low and high have been rearranged so that
their keys are sorted into nondecreasing order.
Uses: The contiguous list
*/
{
if(high>low){
recursive_merge_sort(low,(high+low)/2);
recursive_merge_sort((high+low)/2+1,high);
merge(low,high);
}
}
template<class Record>
void Sortable_list<Record>::merge_sort()
/* Post: The entries of the sortable list have been rearranged so that
their keys are sorted into nondecreasing order.
Uses: The contiguous list
*/
{
recursive_merge_sort(0,size()-1);
}
【实验结果】

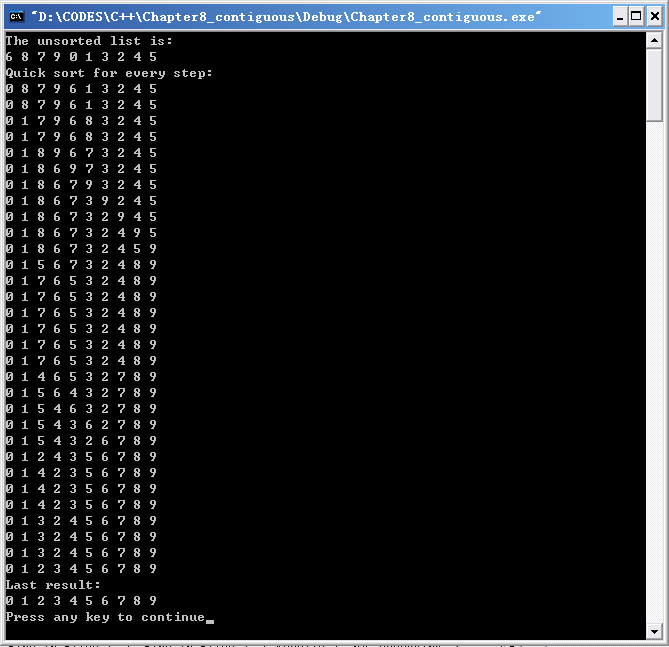
快速排序
快速排序是对冒泡排序的一种改进。
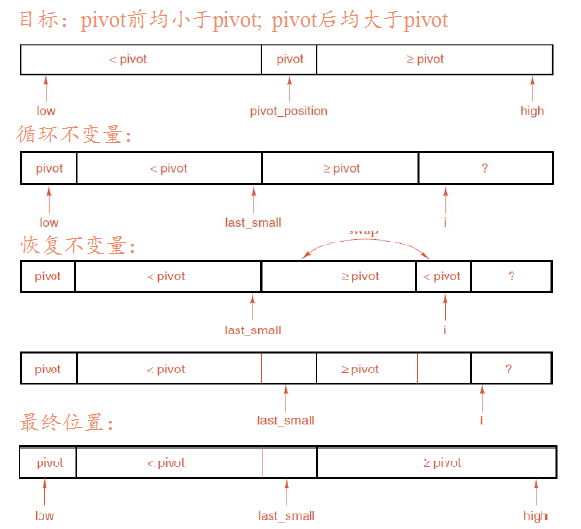
快速排序算法的基本思想是:每一趟排序中找一个点pivot,将表分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分的所有Record都比pivot小,另一部分比pivot大,然后再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序。?

【相关实验】
1.仍旧使用上述的Sortable_list。
2.根据快速排序的思想,每趟排序将表分成两部分然后仍旧进行快速排序,所以可以通过递归实现,而为了调用递归函数,我们首先编写给定要排序范围的参数的函数recursive_quick_sort(int low,int high)//之所以不将开始的quick_sort直接写作递归函数,是为了避免输入参数而方便用户调用。另外需要一个partition函数,返回每趟排序之后的分点。
3.为了输出每趟排序,我的想法是在每次递归中使用traverse(print_out)输出,但却不是想象的结果。因为递归是每次递归出来之后才执行函数print_out,除了前几次可以看到结构,后来都是在排序好之后…所以我们仍旧通过swap函数实现输出。
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print
?
- template<class?Record>??
-
int?Sortable_list<Record>::partition(int?low,int?high)??
-
/*Pre:??low?and?high?are?valid?positions?of?the?Sortable_list,?with?low<=high.?
- ??Post:?The?center?(or?left?center)?entry?in?the?range?between?indices?low?and??
- ????????high?of?the?Sortable_list?has?been?chosen?as?a?pivot.?All?entries?of?the?
- ????????Sortable_list?between?indices?low?and?high,?inclusive,?have?been?rearranged?
- ????????so?that?chosen?with?keys?less?than?the?pivot?com?before?the?pivot?
- ????????and?the?remaining?entries?come?after?the?pivot.?The?final?position?of?the??
- ????????pivot?is?returned.?
- ?Uses:?swap(int,int?j)?contigious?list?
- */??
- {??
- ????Record?pivot;??
-
????int?i,???????????//used?to?scan?through?the?list??
-
????????last_small;??//position?of?the?last?key?less?than?pivot??
- ????swap(low,(low+high)/2);??
- ????pivot=entry[low];??
- ????last_small=low;??
-
????for(i=low+1;i<=high;i++)??
-
????//At?the?beginning?of?each?iteration?of?this?loop,?we?have?the?following?conditions:??
-
????//????If?low<j<=last_samll?then?entry[j].key<pivot??
-
????//????If?last_small<j<i?then?entry[j].key>=pivot.??
-
???????if(entry[i]<pivot){??
- ???????????last_small=last_small+1;??
-
???????????swap(last_small,i);??//Move?large?entry?to?right?and?small?to?left??
- ???????}??
-
????swap(low,last_small);???//Put?the?pivot?into?its?proper?position.??
-
????return?last_small;??
- }??
- ??
-
template<class?Record>??
-
void?Sortable_list<Record>::recursive_quick_sort(int?low,int?high)??
-
/*Pre:??low?and?high?are?valid?positions?in?the?Sortable?list.?
- ??Post:?The?entries?of?the?Sortable_list?have?been?rearranged?so?that?their?keys?
- ????????are?sorted?into?nondecreasing?order.?
- ??Uses:?The?contiguous?list,?recursive_quick_sort,?partition.?
- */??
- {??
-
????int?pivot_postion;??
-
????if(low<high){??
- ????????pivot_postion=partition(low,high);??
- ????????recursive_quick_sort(low,pivot_postion-1);??
- ????????recursive_quick_sort(pivot_postion+1,high);??
- ????}??
- }??
- ??
-
template<class?Record>??
-
void?Sortable_list<Record>::quick_sort()??
- {??
- ????recursive_quick_sort(0,count-1);??
- }??
-
//其他函数见源码??
template<class Record>
int Sortable_list<Record>::partition(int low,int high)
/*Pre: low and high are valid positions of the Sortable_list,with low<=high.
Post: The center (or left center) entry in the range between indices low and
high of the Sortable_list has been chosen as a pivot. All entries of the
Sortable_list between indices low and high,inclusive,have been rearranged
so that chosen with keys less than the pivot com before the pivot
and the remaining entries come after the pivot. The final position of the
pivot is returned.
Uses: swap(int,int j) contigious list
*/
{
Record pivot;
int i,//used to scan through the list
last_small; //position of the last key less than pivot
swap(low,(low+high)/2);
pivot=entry[low];
last_small=low;
for(i=low+1;i<=high;i++)
//At the beginning of each iteration of this loop,we have the following conditions:
// If low<j<=last_samll then entry[j].key<pivot
// If last_small<j<i then entry[j].key>=pivot.
if(entry[i]<pivot){
last_small=last_small+1;
swap(last_small,i); //Move large entry to right and small to left
}
swap(low,last_small); //Put the pivot into its proper position.
return last_small;
}
template<class Record>
void Sortable_list<Record>::recursive_quick_sort(int low,int high)
/*Pre: low and high are valid positions in the Sortable list.
Post: The entries of the Sortable_list have been rearranged so that their keys
are sorted into nondecreasing order.
Uses: The contiguous list,recursive_quick_sort,partition.
*/
{
int pivot_postion;
if(low<high){
pivot_postion=partition(low,high);
recursive_quick_sort(low,pivot_postion-1);
recursive_quick_sort(pivot_postion+1,high);
}
}
template<class Record>
void Sortable_list<Record>::quick_sort()
{
recursive_quick_sort(0,count-1);
}
//其他函数见源码
【实验结果】

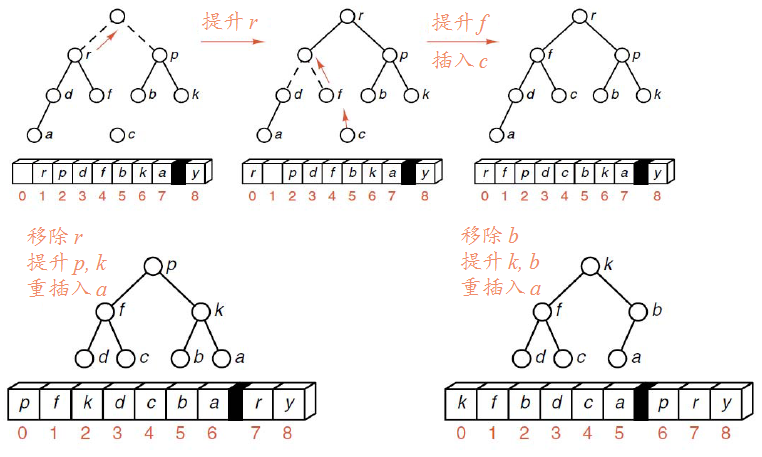
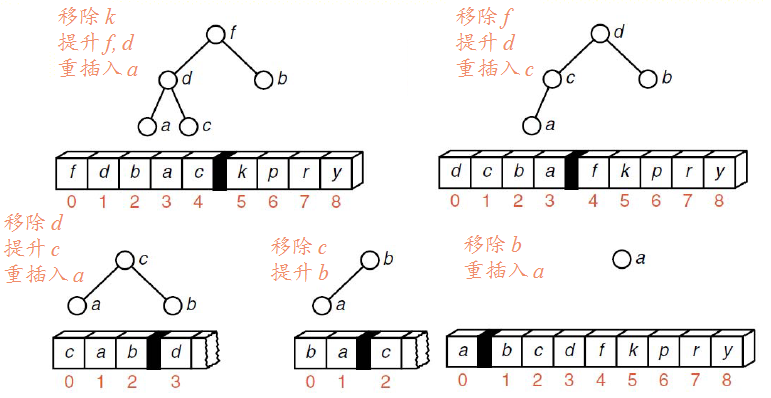
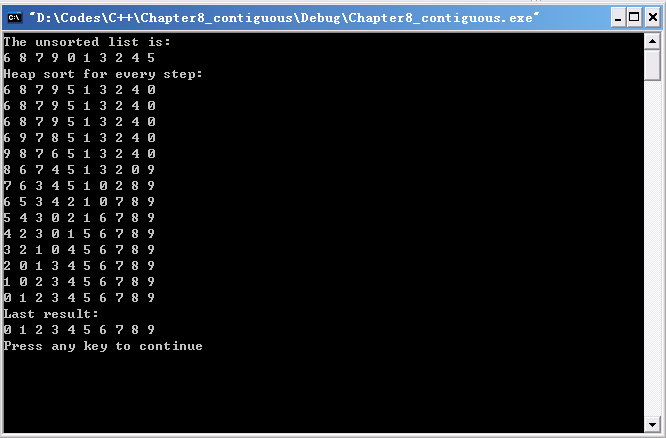
堆排序
堆排序是先将表中Record按大堆(或小堆)存放,使选取最大的Record变的极为容易,每次选取之后再提升堆。实现排序。

继续:

【相关实验】
1.仍旧使用上述的Sortable_list。
2.编写heap_sort()函数。按思路,首先应该建堆,然后取堆顶元素,之后对剩下元素重新建堆(提升堆),所以我们需要编写build_heap()函数,其通过inster_heap函数将元素一个个插入堆中。
最后实现heap_sort函数。
3.我们在每次插入堆时调用traverse(print_sort)实现对每趟排序的输出。
[cpp]
view plain
copy
print
?
- template<class?Record>??
-
void?Sortable_list<Record>::insert_heap(const?Record?¤t,int?low,int?high)??
-
/*Pre:??The?entries?of?the?Sortable_list?between?indices?low+1?and?high,?
- ????????inclusive,form?a?heap.?The?entry?in?position?low?will?be?discarded.?
- ??Post:?The?entry?current?has?been?inserted?into?the?Sortabl_list?and?the?entries,?
- ????????rearranged?so?that?the?entries?between?indices?low?and?high,?inclusive?
- ????????form?a?heap.?
- */??
- {??
-
????int?large;???????//position?of?child?of?entry[low]?with?the?larger?key??
-
????large=2*low+1;???//large?is?now?the?left?child?of?low??
-
????while(large<=high){??
-
????????if(large<high&&entry[large]<entry[large+1])??
-
????????????large++;????//large?is?now?the?child?of?low?with?the?largest?key.??
-
????????if(current>=entry[large])??
-
????????????break;??????//current?belongs?in?position?low??
-
????????else{???????????//Promote?entry[large]?and?move?down?the?tree???
- ????????????entry[low]=entry[large];??
- ????????????low=large;??
- ????????????large=2*low+1;??
- ????????}??
- ????}??
- ????entry[low]=current;??
- ????traverse(print_out);??
- ????cout<<endl;??
- }??
- ??
-
template<class?Record>??
-
void?Sortable_list<Record>::build_heap()??
-
/*Post:?The?entries?of?the?Sortable_list?have?been?rearranged?so?that??
- ????????it?becomes?a?heap?
- ??Uses:?The?contiguous?list?and?insert_heap?
- */??
- {??
-
????int?low;??
-
????for(low=count/2-1;low>=0;low--){??
- ????????Record?current=entry[low];??
- ????????insert_heap(current,low,count-1);??
- ????}??
- }??
- ??
-
template<class?Record>??
-
void?Sortable_list<Record>::heap_sort()??
-
/*Post:?The?entries?of?the?Sortable_list?have?been?rearranged?so?that?their?keys?
- ????????are?sorted?into?nondecreasing?order.?
- ??Uses:?The?contiguous?list,?build_heap,?insert_heap?
- */??
- {??
-
????Record?current;???????//temporary?storage?for?moving?entries??
-
????int?last_unsorted;????//Entries?beyond?last_unsorted?have?been?sorted.??
-
????build_heap();?????????//First?phase:?Turn?the?list?into?a?heap??
-
????for(last_unsorted=count-1;last_unsorted>0;last_unsorted--){??
-
????????current=entry[last_unsorted];???//Extract?the?last?entry?from?the?list??
-
????????entry[last_unsorted]=entry[0];??//Move?top?of?heap?to?the?end??
-
????????insert_heap(current,last_unsorted-1);??//Restore?the?heap??
- ????}??
- }??
-
//其他函数见源码??
template<class Record>
void Sortable_list<Record>::insert_heap(const Record ¤t,int low,int high)
/*Pre: The entries of the Sortable_list between indices low+1 and high,form a heap. The entry in position low will be discarded.
Post: The entry current has been inserted into the Sortabl_list and the entries,rearranged so that the entries between indices low and high,inclusive
form a heap.
*/
{
int large; //position of child of entry[low] with the larger key
large=2*low+1; //large is now the left child of low
while(large<=high){
if(large<high&&entry[large]<entry[large+1])
large++; //large is now the child of low with the largest key.
if(current>=entry[large])
break; //current belongs in position low
else{ //Promote entry[large] and move down the tree
entry[low]=entry[large];
low=large;
large=2*low+1;
}
}
entry[low]=current;
traverse(print_out);
cout<<endl;
}
template<class Record>
void Sortable_list<Record>::build_heap()
/*Post: The entries of the Sortable_list have been rearranged so that
it becomes a heap
Uses: The contiguous list and insert_heap
*/
{
int low;
for(low=count/2-1;low>=0;low--){
Record current=entry[low];
insert_heap(current,count-1);
}
}
template<class Record>
void Sortable_list<Record>::heap_sort()
/*Post: The entries of the Sortable_list have been rearranged so that their keys
are sorted into nondecreasing order.
Uses: The contiguous list,build_heap,insert_heap
*/
{
Record current; //temporary storage for moving entries
int last_unsorted; //Entries beyond last_unsorted have been sorted.
build_heap(); //First phase: Turn the list into a heap
for(last_unsorted=count-1;last_unsorted>0;last_unsorted--){
current=entry[last_unsorted]; //Extract the last entry from the list
entry[last_unsorted]=entry[0]; //Move top of heap to the end
insert_heap(current,last_unsorted-1); //Restore the heap
}
}
//其他函数见源码
【实验结果】

结果分析
【希尔排序】 1.希尔排序是直接插入的一种改进,在效率上较直接插入排序有较大的改进。
直接插入排序每次只能将Record移动一个位置,即增量increment为1,而希尔排序开始时增量较大,分组较多,每组Record数目少,故各组内直接插入较快;increment递减之后分组逐渐减少,Record增多,但由于已经在increment较大时进行过排序,表更接近于有序状态,新一趟的排序也较快。
2.我在实验中子表的排序是通过定义一个新表,然后调用直接插入函数。但这种方法效率并不高,而且浪费空间;直接对子表进行直接插入的排序是一种更好的方法。
3.希尔排序复杂度为:O(nlog2n) ? d =1希尔与直接插入排序基本一致
4.希尔排序是不稳定的排序算法,即相等元素的顺序可能改变
【归并排序】 1.归并排序在实现上用链式表更为合理,因为合并中需要定义新的表,即使我们通过动态定义再删除,以节省不必要的空间,这些工作仍是有些费时。而链式表只是返回指针,对节点Node的Node<Node_entry>*next部分进行操作,不需要数据的移动。但同时链式表的使用也需要对指针有熟悉的掌握,很容易出错,先画图再编码往往会有更清晰的思路。
2.归并排序的复杂度为:O(nlog2n)
3.归并排序是稳定的排序算法,即相等元素的顺序不会改变
【快速排序】 1.复杂度:最好 O(nlog2n),最坏 O(n2)
2.快速排序的最坏情况基于每次划分对主元的选择。基本的快速排序选取第一个元素作为主元。这样在数组已经有序的情况下,每次划分将得到最坏的结果。一种比较常见的优化方法是随机化算法,即随机选取一个元素作为主元。这种情况下虽然最坏情况仍然是O(n^2),但最坏情况不再依赖于输入数据,而是由于随机函数取值不佳。
3.快速排序是一种不稳定的排序算法
【堆排序】 1.实现堆排序很重要的一个操作就是建堆
要将初始表调整为一个大根堆,就必须将它所对应的完全二叉树中以每一结点为根的子树都调整为堆。显然只有一个结点的树是堆,而在完全二叉树中,所有序号大于n/2的结点都是叶子,因此以这些结点为根的子树均已是堆。这样,我们只需依次将以序号为n/2,…,1的结点作为根的子树都调整为堆即可。
2.堆[排序的时间,主要由建立初始堆和反复重建堆这两部分的时间开销构成,堆排序的最坏时间复杂度为O(nlog2n)。
3.堆排序是不稳定的排序算法
4.由于建初始堆所需的比较次数较多,所以堆排序不适宜于记录数较少的文件。
堆排序每次在大堆中直接选择出顶即最大的元素,这与选择排序极为相似,但他们是不同的,堆排序的性能更为优越。因为选择排序中,为了从表中选出最小的记录,必须进行n-1次比较,然后在剩余表中选出关键字最小的记录,又需要做n-2次比较。事实上,后面的n-2次比较中,有许多比较可能在前面的n-1次比较中已经做过,但由于前一趟排序时未保留这些比较结果,所以后一趟排序时又重复执行了这些比较操作。堆排序可通过树形结构保存部分比较结果,可减少比较次数。
原文地址:http://www.voidcn.com/article/p-ucctzjhq-vo.html
(编辑:ASP站长网)
|

 Redis未授权检测漏洞G
Redis未授权检测漏洞G 严峻Web对抗环境下的W
严峻Web对抗环境下的W 遭黑客盗走AMD GPU 部
遭黑客盗走AMD GPU 部 企业级信息防泄漏大方
企业级信息防泄漏大方